This project focuses on predicting and classifying arrhythmias using various machine learning algorithms. The dataset used for this project is from the UCI Machine Learning Repository, which consists of 452 examples across 16 different classes. Among these, 245 examples are labeled as "normal," while the remaining represent 12 different types of arrhythmias, including "coronary artery disease" and "right bundle branch block."
- Number of Examples: 452
- Number of Features: 279 (including age, sex, weight, height, and various medical parameters)
- Classes: 16 total (12 arrhythmia types + 1 normal group)
Objective:
The goal of this project is to predict whether a person is suffering from arrhythmia, and if so, classify the type of arrhythmia into one of the 12 available groups.
To address the classification task, the following machine learning algorithms were employed:
- K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) Classifier
- Logistic Regression
- Decision Tree Classifier
- Linear Support Vector Classifier (SVC)
- Kernelized Support Vector Classifier (SVC)
- Random Forest Classifier
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA) (for dimensionality reduction)
- Analyzed the 279 features to identify patterns and correlations that could help with prediction.
- Addressed the challenge of the high number of features compared to the limited number of examples by employing PCA.
- Handled missing values, standardized data, and prepared it for machine learning models.
- Applied Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to reduce the feature space and eliminate collinearity, improving both execution time and model performance.
- Trained various machine learning algorithms on the dataset.
- Evaluated model performance using accuracy, recall, and other relevant metrics.
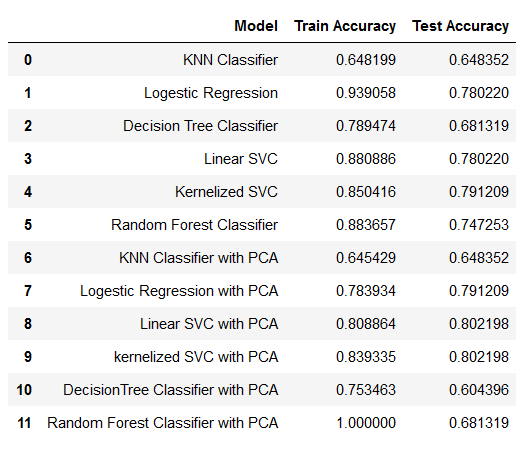
- PCA helped reduce the complexity of the dataset, leading to improved model accuracy and reduced overfitting.
- After applying PCA, models were retrained, and significant improvements were observed.
Applying Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to the resampled data significantly improved the performance of the models. PCA works by creating non-collinear components that prioritize variables with high variance, thus reducing dimensionality and collinearity, which are key issues in large datasets. PCA not only enhanced the overall execution time but also improved the quality of predictions.
- The best-performing model in terms of recall score is the Kernelized Support Vector Machine (SVM) with PCA, achieving an accuracy of 80.21%.
- Experiment with more advanced models like XGBoost or Neural Networks.
- Perform hyperparameter tuning to further improve model accuracy and recall.
- Explore feature selection techniques alongside PCA to refine the feature set.
This README.md offers clear documentation of the objectives, algorithms used, results, and the significance of PCA in your project. It also provides essential information on how to run the project and the prerequisites.